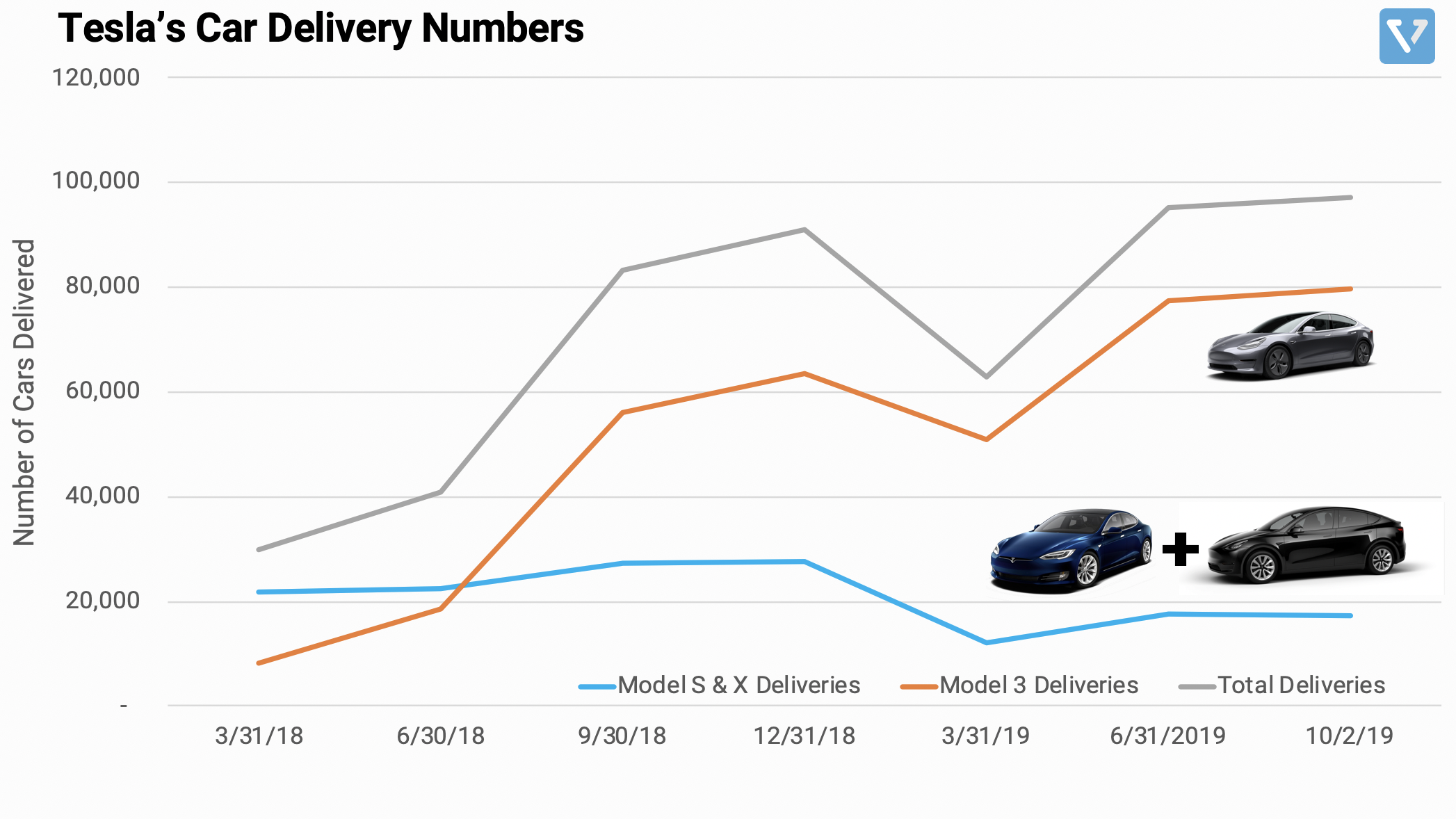
Figure 1: Tesla’s car delivery numbers (quarterly basis). After a weak Q1 2019 (March 2019), the company delivered strong delivery numbers in Q2 and Q3 of this year.
Tesla’s share price has gone up ~11% from its low in October. The company recently reported strong car delivery numbers (see Figure 1 for Tesla’s quarterly car delivery numbers). The number of delivered cars is an important metric for Tesla, as it is a leading indicator for revenue. Cars that are delivered to consumers result in revenue in the following quarters. After a weak Q1 2019, the company delivered strong delivery numbers in Q2 and Q3 of this year (stay tuned for the earning release this upcoming week). Despite this positive trend, Tesla may face strong headwinds internationally:
- Weakening consumer demand in China. China is the largest electric car market in the world. Chinese consumers buy about 60% of all electric cars manufactured worldwide. However, faced with slowing economic growth, electric car sales in China has dropped 34.2% compared to the same period last year. This may affect Tesla’s sales in the country. Currently, the company generates about 13% of its revenue from sales in China (a number that was growing 50% year over year). A slowdown in sales in China can affect Tesla’s revenue.
- Tariffs from the trade war. Starting in December, China plans to impose a 25% tariff on US cars sold there. This may force Tesla to increase prices.
- Stronger Dollar. Between August to mid October, the Yuan exchange rate against the US dollar has weakened by ~7%. A stronger dollar means that Tesla’s car is more expensive in China.









