Invest in 10,000+ US Stocks and ETFs
* Offering through VF Securities, Inc. (member FINRA/SIPC)

Disclosure: Companies shown are meant to a representative sample of stocks available and not a recommendation to purchase.



Read about experiences of those who have taken their portfolio global with Vested
Disclosure: These customers were not paid for their testimonials and may not be representative of the experience of other customers. These testimonials are no guarantee of future performance or success.

Learn about the world of alternative assets with our in-depth educational modules on US Stocks, P2P Lending, INR Bonds and more
Start Learning
Get answers to frequently asked questions by our investors or get help on any topic
Get in touch
Stay up to date on the latest investing trends in the markets and other announcements from Vested
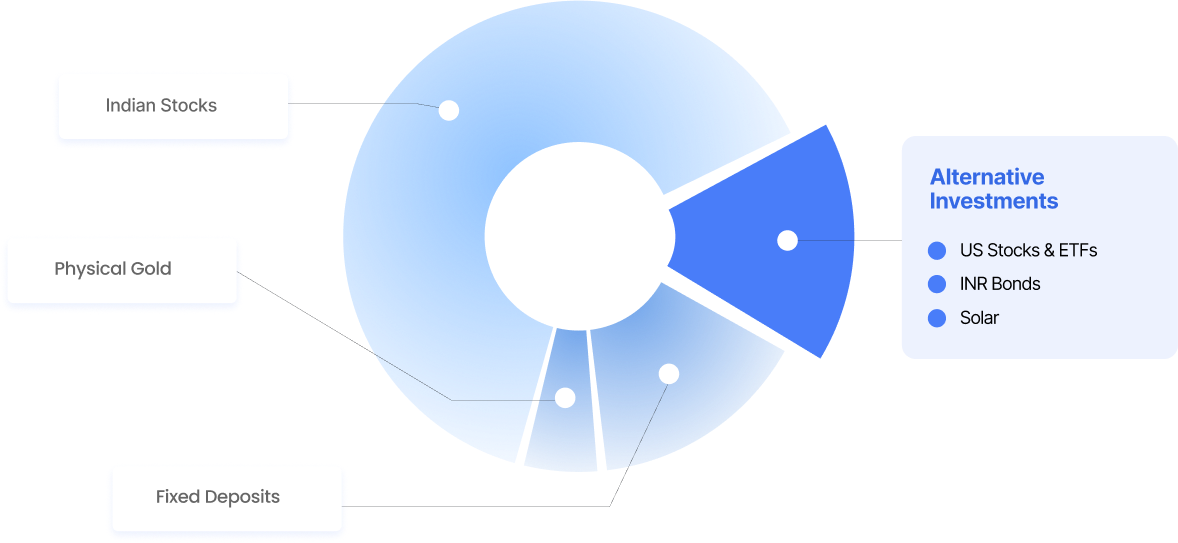
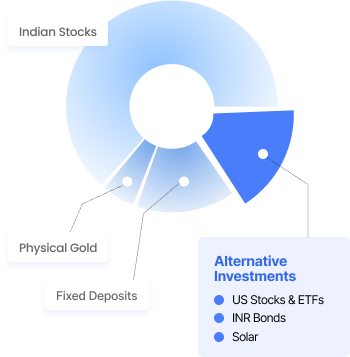
Browse ArticlesAlternative investments are non-traditional financial assets that exist outside of conventional options, such as Indian stocks, fixed deposits, physical gold, and cash. They offer diversification opportunities into new-age asset classes and help investors build a more balanced portfolio.
Vested is a comprehensive platform for investing in alternative assets, facilitating diverse and global investment opportunities.
At Vested, the alternative investment options include:
The alternative investments offered on Vested are legal and follow the guidelines set by the regulators (the RBI and SEBI). Before you venture into the world of alternatives, it is vital to consider the following points:
Understanding the investment: Before investing, you should have a clear understanding of the asset class, its structure, and potential risks and returns. This includes understanding the market dynamics, historical performance, and factors influencing the asset’s value. It’s essential to ensure that they align with your overall investment strategy and risk tolerance
Liquidity: Alternative investments often have lower liquidity compared to traditional investments. You must consider your liquidity needs and whether you can afford to have your money tied up for the investment period.
Vested is accessible to Indian residents, allowing them to invest in US stocks and ETFs, as well as alternative investment options like P2P lending and INR bonds. It’s suitable for both beginners and experienced investors who are looking for opportunities to invest in global markets and non-traditional assets.
Non-resident Indians (NRIs) can also invest in US Stocks with Vested. To open an account with Vested, NRIs need to provide their PAN card or passport, proof of address like a passport, and their tax ID from the country where they are currently a tax resident.
To open an account on Vested as an investor, follow these steps:
Your assets are held at a 3rd party custodian, and we do not ever touch or hold your money.
For US Stocks, If Vested shuts down, you would still have access to all your cash and securities, as we will ensure that direct DriveWealth access is established for you to continue to buy or sell securities. In the highly unlikely event that Vested and DriveWealth shut down, your SIPC insurance kicks in. Each brokerage account opened with Vested is insured by SIPC (Securities Investor Protection Corporation) up to $500,000. This includes $250,000 in cash. For more details, please read here
For other asset classes – Vested Edge and INR Bonds, you will still have access to your cash and securities through our NBFC-P2P partners (for Vested Edge), and your INR Bonds holdings will persist in your demat account with NSDL/CDSL.
Vested offers two plans, Basic and Premium, with different fee structures:
Basic Plan
Premium Plan