A stock index is a collection of stocks that are grouped together to represent a specific market or sector. The index provides a benchmark for investors to track the performance of the overall market or sector. Indices are not investible directly. Most investors invest in either mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track and mimic certain indices.
Dow Jones Industrial Average
What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
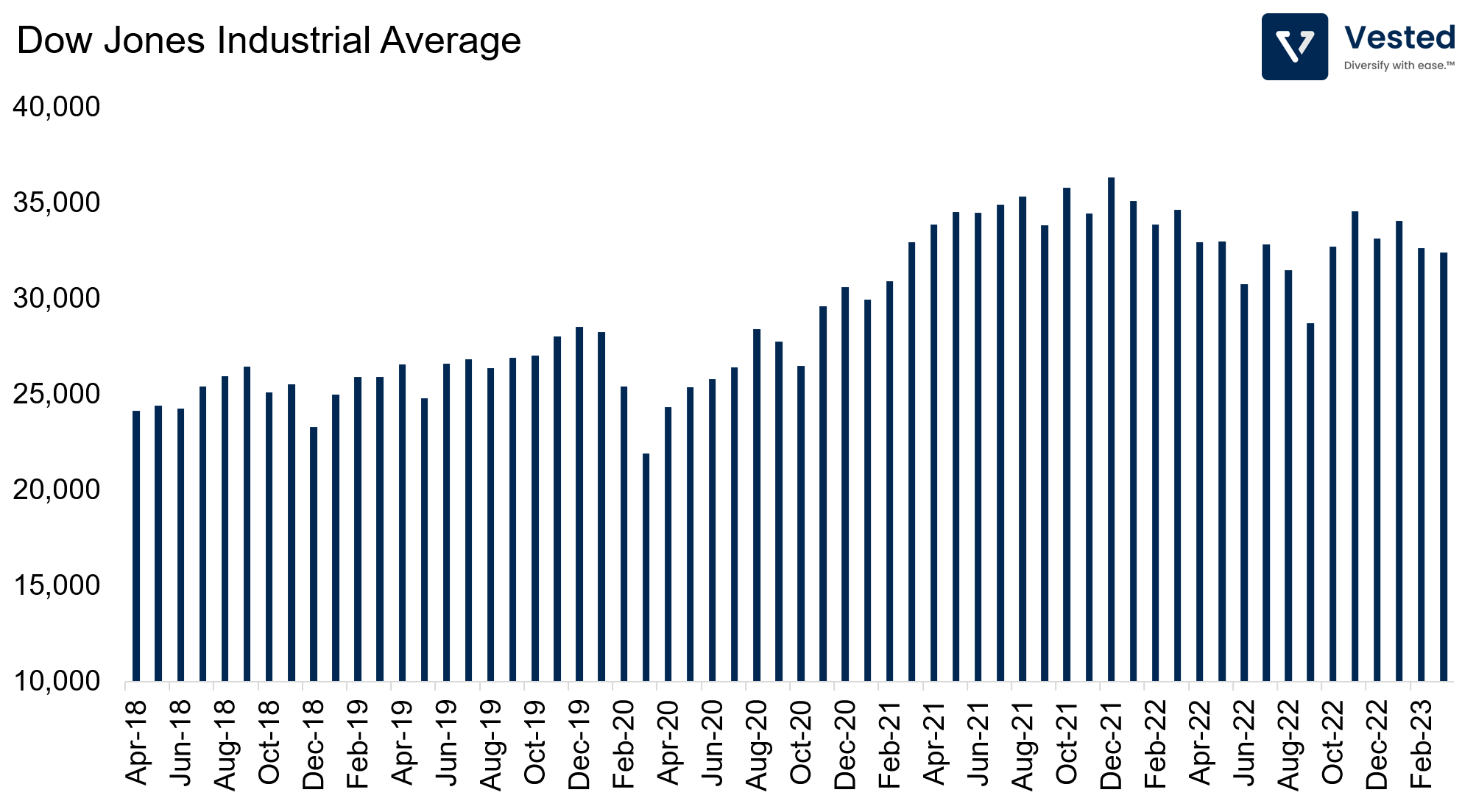
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, also known as the Dow or DJIA, is one of the world’s oldest and most well-known stock indices. In 1896, Charles Dow created his first stock average comprising 12 industrial companies. None of the original 12 are currently part of the index. Currently, the DJIA is made up of 30 large, publicly-traded companies in the US. These companies are chosen by the editors of The Wall Street Journal based on their overall market capitalization, business sector, and financial stability.
The DJIA is calculated by taking the sum of the stock prices of the 30 companies and dividing it by the Dow Divisor, which is adjusted for stock splits and other changes in the index. As of this writing, the Dow Divisor is approximately 0.15. The DJIA is often used as a barometer for the overall health of the US stock market and is closely watched by investors worldwide.
However, critics of the DJIA believe that the number of companies is insufficient and smaller companies are neglected. Furthermore, since the index is price-weighted, it does not take market capitalization into consideration. A smaller company with a bigger stock price weighs more than a bigger company with a smaller stock price.
How can I invest in the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
You can purchase shares of the 30 companies in the DJIA in proportion to their weighting in the index. However, you would also have to replace companies periodically as the index changes. This would be too time-consuming and is not a feasible strategy for most investors. Instead, you can invest in the DJIA through ETFs.
| Name | Ticker | Expense Ratio | Provider |
| SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF | DIA | 0.16% | State Street Global Advisors |
| iShares Dow Jones U.S. ETF | IYY | 0.20% | BlackRock |
| ProShares Ultra Dow30 | DDM | 0.95% | ProShares |
S&P 500
What is the S&P 500?
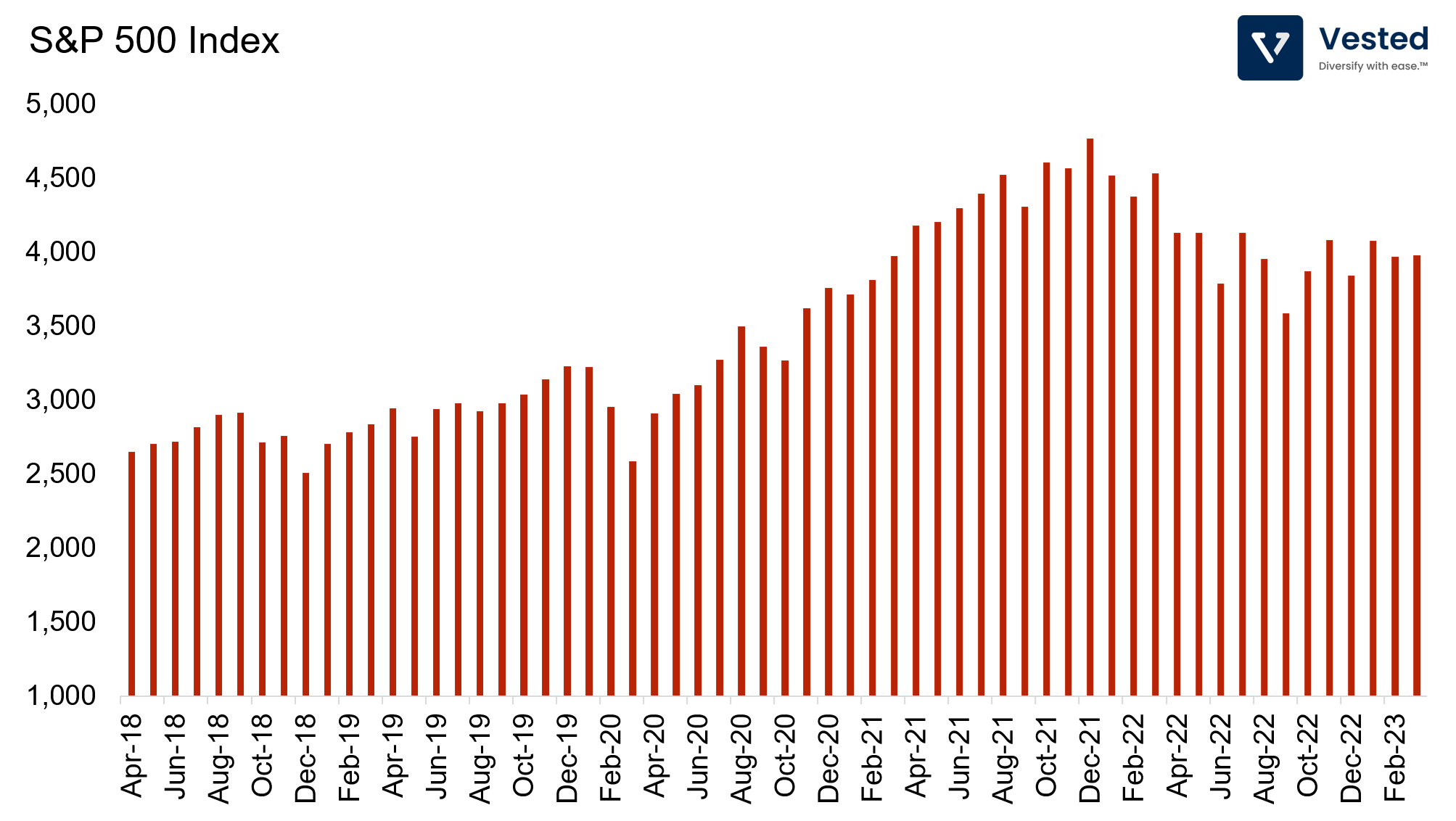
The Standard and Poor’s (S&P) 500 is another popular stock index in the US. Created in 1957 by a credit rating agency known as Standard and Poor’s Corp., the S&P 500 is made up of 500 large-cap stocks from various industries in the US. Companies are required to have positive earnings in the trailing four quarters to be included in the index.
The index is calculated by adding up the adjusted market caps of all the companies included and dividing the sum by a divisor. This divisor is confidential information owned by the S&P Dow Jones Indices and is not disclosed to the public.
The index is weighted by market capitalization, meaning stock prices of bigger companies like Apple and Microsoft have a bigger impact on the index than smaller companies. As a result, the S&P 500 does not include smaller companies, which historically have had better returns.
The S&P 500 includes more companies and covers a broader range of industries compared to the DJIA. The index is widely used as a benchmark for mutual funds and other investment products.
How can I invest in the S&P 500?
Although it’s possible to purchase individual shares of 500 companies listed on the S&P 500, most investors do not follow that route. Rather, they invest in mutual funds and ETFs.
| Name | Ticker | Expense Ratio | Provider |
| Fidelity 500 Index Fund | FXAIX | 0.02% | Fidelity |
| iShares Core S&P 500 ETF | IVV | 0.03% | BlackRock |
| Vanguard S&P 500 ETF | VOO | 0.03% | Vanguard |
| SPDR Portfolio S&P 500 ETF | SPLG | 0.03% | State Street Global Advisors |
| SPDR S&P 500 ETF | SPY | 0.09% | State Street Global Advisors |
Nasdaq Composite
What is the Nasdaq Composite Index?
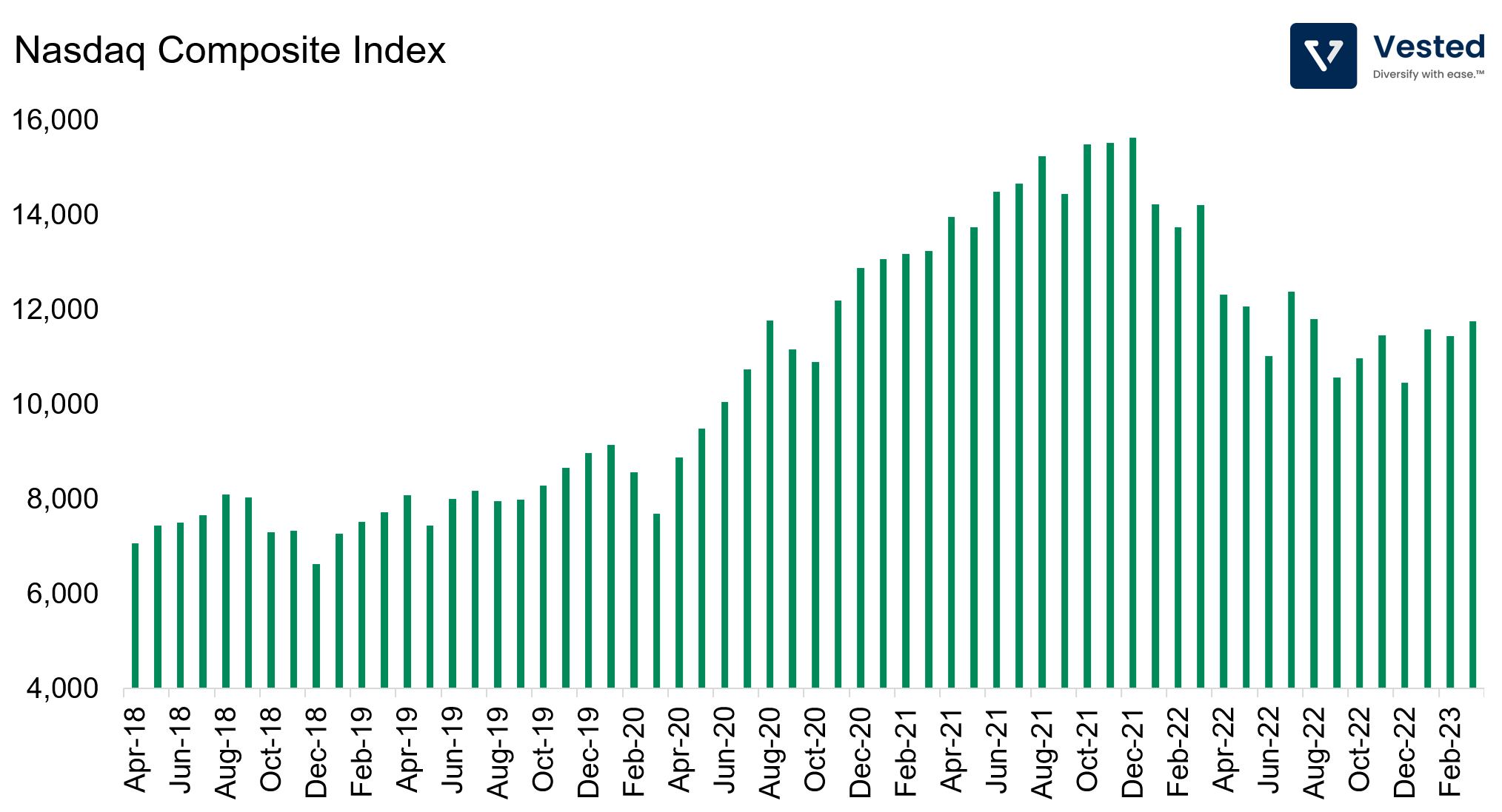
The Nasdaq Composite is a stock index that includes all the stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange. Created in 1971, the Nasdaq Composite is known for its heavy weighting in technology and internet-related companies. As a result, it has many smaller technology stocks not represented in the DJIA or S&P 500. However, it is less diversified than the other indices due to its focus on technology and growth-oriented stocks. The Nasdaq index is made up of more than 3,700 stocks.
The Nasdaq Composite was originally launched with an index value of 100 and is calculated using a market capitalization-weighted methodology similar to the S&P 500. As a result, it is also heavily weighted at the top. The index is often used as a benchmark for technology stocks and is closely watched by investors in the technology sector.
How can I invest in the Nasdaq Composite?
Due to the large number of stocks listed on the Nasdaq, it is impossible for retail investors to keep track of all of them. However, since the index is top-heavy, five mega-cap companies constitute more than 40% of the index. These companies are Apple Inc (12.25%), Microsoft Corp. (9.93%), Google (7.38%), Amazon.com, Inc. (7.13%), and Tesla Inc (4.79%).
To invest in the wide array of stocks listed in the index, investors typically choose ETFs. There are a wide variety of ETFs available that focus on specific segments of the Nasdaq. Some of the most popular ones only track the 100 largest, actively traded stocks on the Nasdaq exchange. Here are some examples of Nasdaq ETFs:
| Name | Ticker | Expense Ratio | Provider |
| INVESCO NASDAQ 100 ETF | QQQM | 0.15% | Invesco |
| Fidelity Nasdaq Composite Index ETF | ONEQ | 0.21% | Fidelity |
| First Trust Nasdaq Cybersecurity ETF | CIBR | 0.60% | First Trust |

